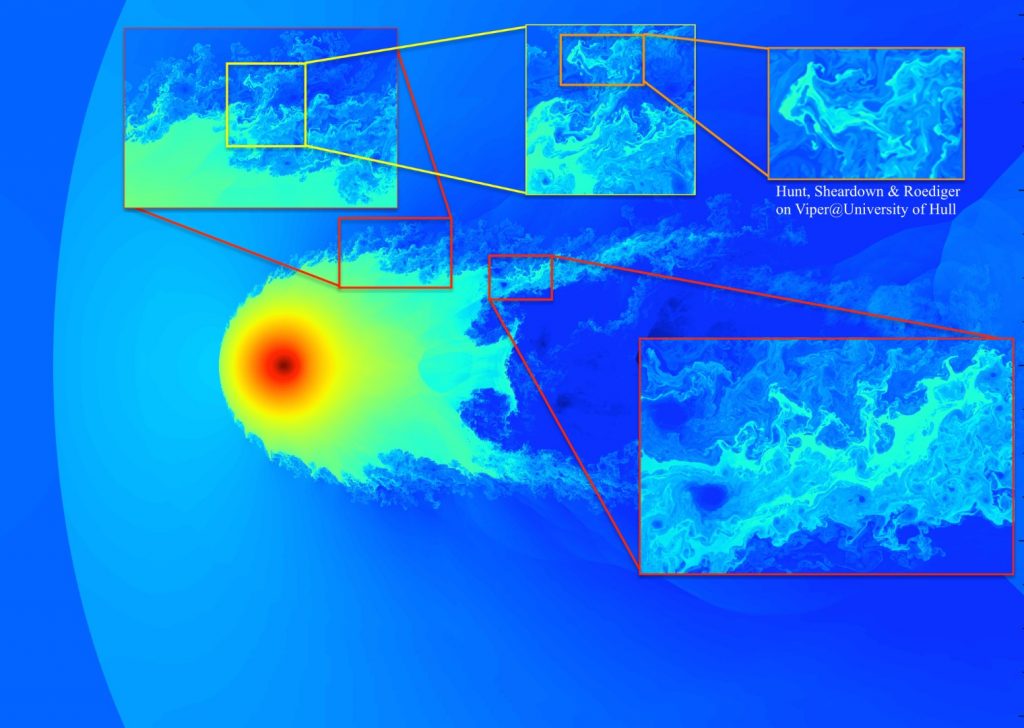
We simulated a spherical galaxy moving through the atmosphere of a galaxy cluster. The colours in the image show the gas density in the simulation grid. The densest gas, shown in dark red, resides in the galaxy centre. The galaxy moves to the left. The head wind that the galaxy experiences strips off the galaxy’s own gas and creates a tail to the right. This 2D simulation reaches a resolution of 8000 grid cells across the galaxy’s atmosphere. Due to this high resolution, the simulation captures mixing features that are more than 1000 times smaller than the galaxy. Some of these are shown in the zoom-ins.
The simulation was performed by Matthew Hunt, Alexander Sheardown and Elke Roediger. It took 24 hours on 3584 computing cores (128 nodes), i.e., in total 86,000 CPU hours.
For further information:
The E.A. Milne Centre for Astrophysics

